Imagine a life where every step you take is confident and steady – that's the power of lower body stability. Lower body balance is a fundamental aspect of physical fitness. It encompasses maintaining equilibrium and stability while performing and engaging in various activities, from basic actions such as walking and ascending stairs to more complex endeavors such as sports and recreational activities. So continue reading to learn the lower body exercises that you can try.
Moreover, whether you're an athlete seeking to improve performance, an older adult aiming to prevent falls, or simply someone enhancing their physical health, understanding the significance of lower body balance is the first step toward achieving a more balanced, healthier life.
Four Simple Exercises for Improved Lower Body Balance
1. Lateral Leg Lifts
Begin in an upright standing position with your feet hip-width apart, maintaining good alignment with your head, shoulders, hips, and legs. Hold your hands together. Engage your core, and slowly lift your left leg to the side while maintaining your right leg straight. Return to the starting position and repeat the movement. Start with 3 sets of 10 repetitions on each side.


2. Single Leg Deadlifts
Firstly, begin in an upright standing position with your feet hip-width apart, maintaining good alignment with your head, shoulders, hips, and legs. Engage your core, transfer all your weight onto one foot, and bend your supporting knee slightly. Secondly, hinge your hips and bend your upper body forward to be parallel to the floor while extending your other leg back. Lastly, return to the starting position and repeat the movement. Start with 3 sets of 10 repetitions on each side.
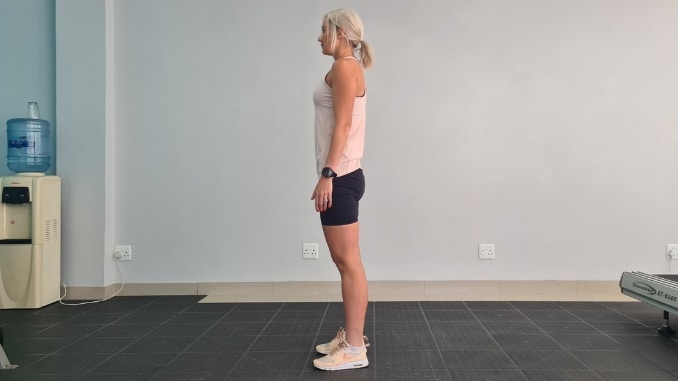

3. Standing Knee Lifts
In this lower body exercises, begin in an upright standing position with your feet hip-width apart, maintaining good alignment with your head, shoulders, hips, and legs. Shift your weight to the right foot, engaging your core. Lift the left knee, ideally to hip height, and hold this position for several seconds. And lastly, lower your left foot back down to the starting position. Start with 3 sets of 10 repetitions on each side.


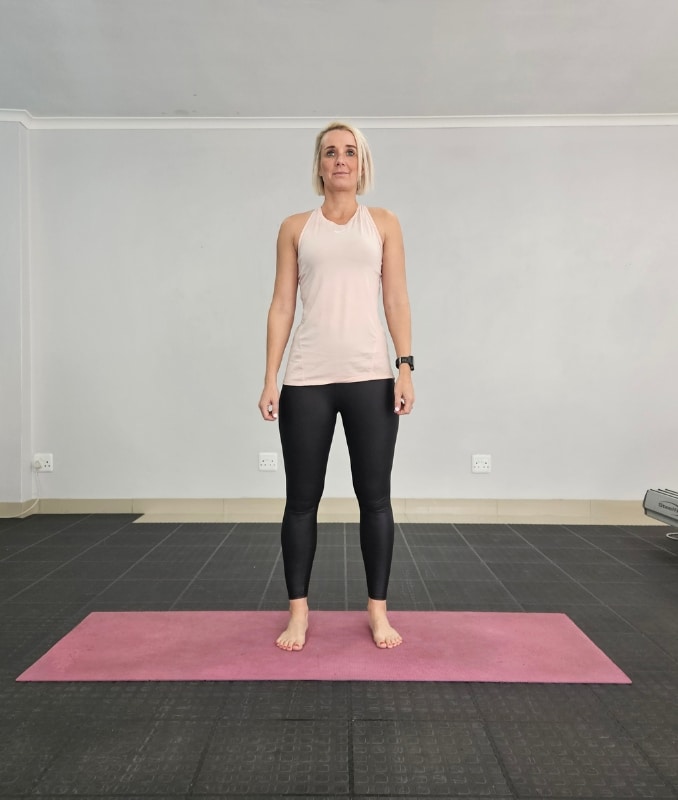
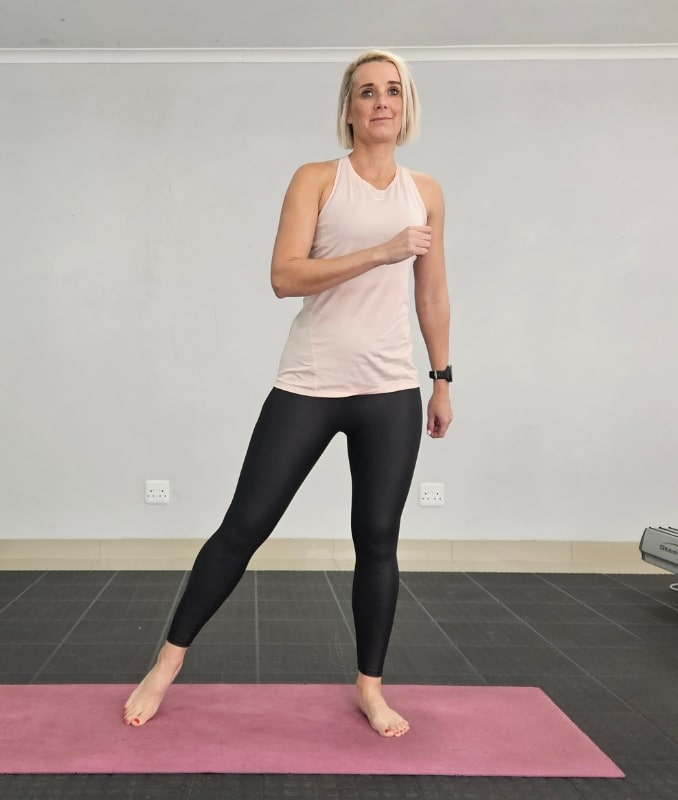
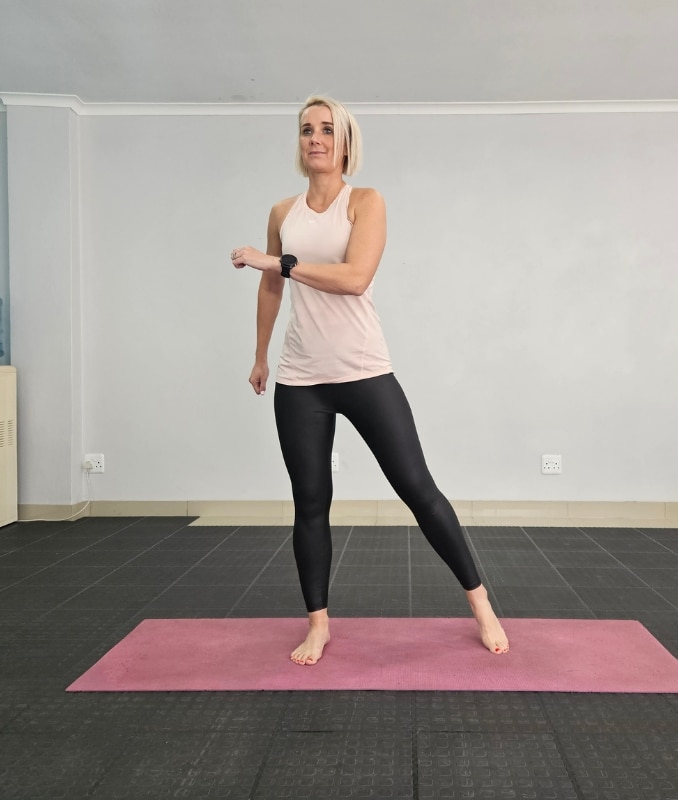
4. Lateral Side Steps
Firstly, begin in an upright standing position with your feet shoulder-width apart, maintaining good alignment with your head, shoulders, hips, and legs. Secondly, place your hands at your sides or clasp them together in front of your body. Lastly, engage your core and take a big step to the side, moving into an alternate side-to-side movement. Start with 3 sets of 10 repetitions on each side.
Moreover, to intensify the movement, add a hopping movement.
 |
 |
 |
Benefits of a Good Balance
-
Reduced Risk of Fall and Injury
Maintaining a good balance helps reduce the risk of falling, especially in older adults. Falls can lead to serious injuries, and good balance can be a critical factor in preventing them. It also helps distribute weight and forces evenly through your body, reducing the risk of overloading and injuring specific muscles or joints.
-
Improved Posture
Good balance promotes proper posture. When your body is in balance, you're less likely to slouch or adopt poor posture habits that can lead to musculoskeletal issues.
-
Enhanced Athletic Performance
Whether you're an athlete or simply enjoy physical activities, a good balance can improve your performance in sports and other physical pursuits. It helps with agility, coordination, and stability, allowing you to move more efficiently.
-
Core Strength
Maintaining balance engages your core muscles, including the abdominals and lower back. This can lead to improved core strength, which is essential for overall stability and preventing lower back pain.
-
Better Mobility and Improved Coordination
Balance training can enhance joint flexibility and mobility. It allows you to move more freely and comfortably during physical activity, which is especially important as you age. Moreover, a good balance is closely linked to coordination. When your balance is on point, you're better able to coordinate different parts of your body, leading to smoother and more precise movements.
-
Better Body Awareness
Exercise often requires a heightened sense of body awareness. This can help you better understand how your body moves and improve your proprioception.
Incorporating balance exercises into your fitness routine, such as yoga, Pilates, stability ball workouts, or specific balance drills, can help you reap these benefits and improve your overall physical well-being. It's worth noting that balance can be developed and maintained at any age, so it's never too late to start working on it.

-
Base of Support
Your feet and legs create the base of support for your entire body. A wider and more stable base of support provides better balance. The positioning of your feet and how they connect with the ground are critical for balance.
-
Muscle Strength
Muscles in the lower body, including the glutes, quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles, help support your body's weight and keep you upright. These muscles contract and work in coordination to stabilize your body.
-
Joint Stability
The lower body joints, such as the hips, knees, and ankles, provide stability and allow for controlled movements. Strong and stable joints are essential for balance, as they resist forces that could cause you to fall.
-
Proprioception
The lower body is rich in proprioceptive sensors, which are responsible for providing information about the position and movement of your body. These sensors are located in muscles, tendons, and joints, particularly in the ankles and feet. Proprioception is crucial for balance, as it allows your body to make quick adjustments to maintain equilibrium.
-
Ankle Control
Ankle strength and mobility are particularly important for balance. The muscles and ligaments around the ankle help control the positioning of the foot and the angle at which it meets the ground. This control is vital for maintaining balance on uneven surfaces.
-
Weight Shifting
When you move or shift your weight, the lower body plays a key role. For example, when you lean forward, your lower body adjusts to keep you from falling. This weight-shifting ability is crucial for maintaining balance in various situations.
-
Core Stability
While not exclusively part of the lower body, the core muscles, including those in the lower back and abdomen, provide a stable foundation for the upper body. A strong core helps distribute forces evenly and supports good posture, which is integral to balance.
-
Alignment
Proper alignment of the lower body, including the hips, knees, and feet, is essential for balance. Misalignment can lead to instability and an increased risk of falling.
Furthermore, to improve and maintain balance, it's crucial to incorporate exercises. During a balance exercise, key muscles and components of the lower body are strengthened and trained. Here are four simple exercises to improve balance:
Conclusion
To sum up, lower body balance is a fundamental aspect of health and physical ability that benefits people of all ages and fitness levels. It plays a crucial role in preventing falls, improving posture, enhancing athletic performance, strengthening the core, and promoting better mobility and coordination. Additionally, balance exercises contribute to better body awareness and proprioception.
Incorporating balance exercises into your fitness routine, such as lateral leg lifts and other similar exercises, can help you develop and maintain good balance. These lower body exercises can be done anywhere and are accessible to people of various fitness levels. However, people with medical conditions need to consult a physical therapist about balance exercises because they have specialized knowledge and can provide tailored guidance for safe and effective workouts. By investing in your balance, you can enjoy a more confident and stable quality of life.